Get insights like this delivered to your inbox
Join 2,500+ GTM professionals. No spam, unsubscribe anytime.
Subscribe to NewsletterWhen integrating with the HubSpot API, the most frequent issues fall into three categories: authentication errors, data mapping problems, and rate limiting challenges. These problems can disrupt workflows, lead to data inconsistencies, and cause delays across sales, marketing, and support teams. Here's a quick breakdown of what you need to know:
- Token Expiry (401 Errors): HubSpot access tokens expire every 30 minutes. Automate token refreshes at least 5 minutes before expiration to prevent downtime.
- Rate Limits (429 Errors): Standard accounts are limited to 100 API requests per 10 seconds. Use batch requests, webhooks, and caching to stay within these limits.
- Field Mapping Errors (400 Errors): Mismatched data types or incorrect property names (e.g., using "Favorite Food" instead of
favorite_food) often cause sync failures. Always validate data formats and fetch property metadata for accurate mapping.
Key Solutions:
- Automate token refresh: Use refresh tokens and distributed locking in multi-server environments.
- Batch updates: Group multiple records into a single API call to reduce request volume.
- Validate data: Ensure correct formats for fields like dates, numbers, and Booleans before syncing.
- Monitor usage: Track API limits and error rates in HubSpot's monitoring tools.
- Handle errors smartly: Use exponential backoff for retries and log errors for debugging.
By addressing these common issues with the right strategies, you can maintain stable integrations and ensure smooth data synchronization.
Mastering HubSpot APIs with Postman: Comprehensive Demo
OAuth Authentication and Token Expiry Problems
One of the most common headaches when working with the HubSpot API is dealing with token expiration. If your integration doesn’t have valid credentials, authentication fails, and everything grinds to a halt. The usual culprit? Expired access tokens. HubSpot access tokens are only valid for 30 minutes (or 1,800 seconds), after which they become unusable. This short lifespan is intentional - it’s a security feature designed to minimize risks if a token gets compromised.
"The access token is what you use for every API request... Here is the catch, though: it expires quickly." - HubSpot Developer Blog
When a token expires, your integration starts throwing 401 Unauthorized errors, and data syncing stops. However, refresh tokens, which remain valid until revoked, allow you to generate new access tokens automatically. Let’s explore why these tokens expire so quickly and how mishandling them can disrupt your integration.
Why Tokens Expire
The 30-minute expiration period is a deliberate balance between security and usability. Problems arise when integrations don’t manage token lifecycles effectively. If you wait until a 401 error occurs to refresh the token, you’re already experiencing downtime. Things get messier in multi-server environments, where multiple servers might attempt to refresh the token simultaneously. This not only wastes API calls but can also hit rate limits. Knowing how token expiration works highlights why proactive management is so important.
How to Manage Token Refresh
To avoid disruptions, calculate the token’s expiration time using Date.now() + expires_in and refresh it at least 5 minutes before it expires. This small buffer ensures you won’t run into failed requests during the transition period.
Here are some best practices for managing tokens:
- Use caching: Store tokens in memory or a tool like Redis to reduce database strain.
- Prevent duplicate refreshes: In multi-server setups, use distributed locking (e.g., Redis SET with NX) to ensure only one server refreshes the token at a time.
- Secure storage: Encrypt tokens with AES-256 or use a secrets manager like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault to keep them safe.
- Handle refresh errors smartly: If a refresh request fails with a 400, 401, or 403 error, it likely means the refresh token is invalid. Stop retrying automatically and prompt the user to reauthorize the integration.
Property Naming and Field Mapping Errors
Getting API integrations right isn’t just about having valid tokens - it’s about ensuring data flows accurately between systems. A big part of this involves proper field mapping. In fact, 75% of rejected migration entries happen because of field mapping errors, like using human-readable labels instead of internal names or mismatching data types.
One common mistake? Using the visible label instead of the internal name. For example, in HubSpot, a property might appear as "Favorite Food" in the interface, but the API expects its internal name, favorite_food. If you send the label instead of the internal name, you’ll get a PROPERTY_DOESNT_EXIST error. To avoid this, always fetch the exact property metadata using the /crm/v3/properties/{objectType} endpoint. This will give you the name, type, and fieldType details needed for accurate mapping.
Another frequent issue is sending data in the wrong format. If HubSpot expects a number but receives a string like "$1,500" with currency symbols or commas, the sync will fail with an INVALID_INTEGER error. Dates also need to follow ISO 8601 (YYYY-MM-DD) or UNIX timestamp formats (in milliseconds), and Boolean fields must be sent as true or false - not 1, 0, Yes, or No. For dropdown fields (enumerations), the value must match one of the predefined internal options exactly, or the request will be rejected.
Here’s a quick guide to common property issues and solutions:
| Property Type | Common Mismatch | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| String | Sending the label instead of the internal name | Use the name from the Properties API |
| Boolean | Using 1, 0, Yes, or No |
Normalize to true or false |
| Date | Wrong timestamp format | Convert to ISO 8601 or UNIX milliseconds (UTC) |
| Enumeration | Value not matching predefined options | Predefine allowed options in HubSpot |
| Number | Including commas or currency symbols | Strip formatting and send plain numbers |
The cost of data quality errors is steep - $12.9 million annually for organizations on average. To minimize these issues, validate a small test batch (just 1–2% of records) before syncing everything. Simple steps like removing special characters from phone numbers, standardizing Boolean values, and formatting dates correctly can significantly reduce errors.
Common Field Mapping Problems
Even experienced developers can run into formatting quirks. For example, when working with multiple checkbox properties, values must be separated by semicolons without spaces (e.g., ;VALUE1;VALUE2). If you’re adding new values to an existing list, don’t forget the leading semicolon - otherwise, you might overwrite existing data.
Phone numbers are another common pain point. HubSpot prefers them in a standardized international format without any special characters like parentheses, dashes, or spaces. So, if your source system stores numbers as (555) 123-4567, you’ll need to strip the formatting before syncing. Additionally, if a required field in HubSpot receives a null or empty value, the sync will stop immediately.
Mapping relationships between objects, like linking contacts to companies, also requires precision. HubSpot allows up to ten unique identifier properties per object (using hasUniqueValue: true). These identifiers can help match records across systems without relying solely on HubSpot’s internal hs_object_id. Incorrect mapping here can leave records orphaned, disconnected from their parent objects.
Setting Up Bidirectional Field Mapping
Now that we’ve covered the common pitfalls, let’s focus on building a strong bidirectional field mapping process. Start by creating a detailed mapping document before writing any code. For each source property, list its HubSpot equivalent, including the internal name, data type, and any transformation logic required. Teams that document their mapping logic can cut deployment delays by 50%, and diagramming object relationships reduces mapping errors by 38%.
Use HubSpot’s Properties API to audit both systems’ property metadata. Identify whether each property should be migrated as-is, transformed (e.g., reformatting dates), ignored, or merged with another field. This audit can help you catch potential validation issues early. You can also use HubSpot’s Property Validations API to set constraints like MIN_LENGTH, MAX_NUMBER, or custom REGEX patterns to reject invalid data.
When it’s time to implement the sync, rely on the /batch/upsert endpoint with unique identifier properties to prevent duplicates. Use transformation scripts to clean up data - strip special characters, normalize Booleans, standardize dates, and validate enumerations.
Always test your mapping logic on a small, controlled batch (1–2% of records) in a sandbox environment before going live. This allows you to identify edge cases, such as empty fields, unexpected data types, or formatting errors, without impacting production data. If you need to clear a property value via the API, send an empty string ("") in your PATCH request - sending null won’t work. And for fields like lifecyclestage, remember that the API only allows forward progression. To move backward, you’ll first need to clear the property.
Rate Limiting and API Throttling
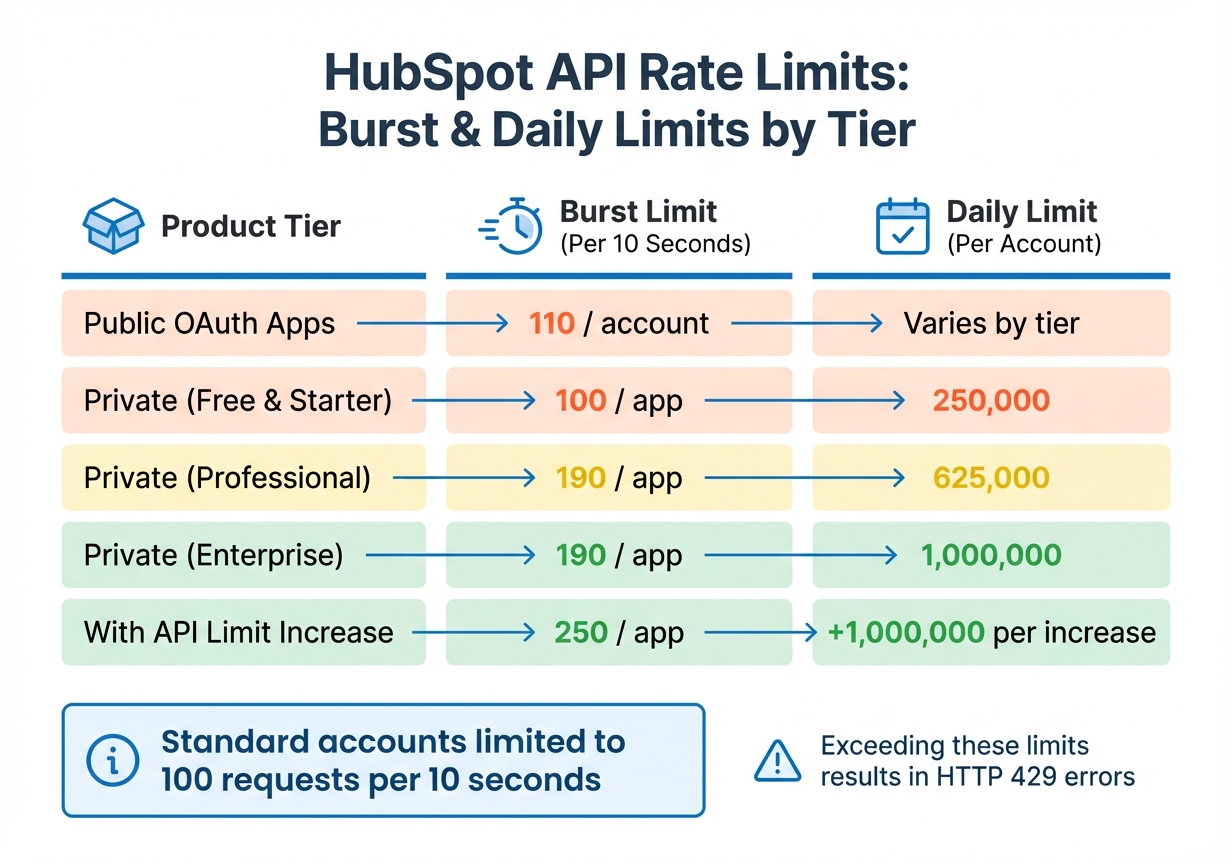
HubSpot API Rate Limits by Product Tier and Account Type
After covering authentication and field mapping, it’s time to address another crucial aspect: managing API call volumes. Even with a solid integration, exceeding request limits can cause everything to grind to a halt. HubSpot enforces two types of limits: burst limits (measured over a 10-second window) and daily limits (reset at midnight per account). If you surpass these thresholds, your requests will be rejected, syncing will pause, and users will experience delays. Staying within these limits is essential to keep data flowing and prevent downtime.
The specific limits depend on your setup. For example, public OAuth apps are capped at 110 requests per 10 seconds. Private apps on Professional or Enterprise tiers can handle 190 requests per 10 seconds, whereas Free and Starter accounts are limited to 100 requests per 10 seconds. Daily limits range from 250,000 calls for Free and Starter accounts to 1,000,000 calls for Enterprise accounts. If you need additional capacity, HubSpot offers an API Limit Increase add-on, which boosts the burst limit to 250 requests per 10 seconds and adds 1,000,000 calls to your daily allowance.
| Product Tier | Burst Limit (Per 10 Seconds) | Daily Limit (Per Account) |
|---|---|---|
| Public OAuth Apps | 110 / account | Varies by tier |
| Private (Free & Starter) | 100 / app | 250,000 |
| Private (Professional) | 190 / app | 625,000 |
| Private (Enterprise) | 190 / app | 1,000,000 |
| With API Limit Increase | 250 / app | +1,000,000 per increase |
How to Detect Rate Limiting
If you hit a burst or daily limit, HubSpot will return an HTTP 429 "Too Many Requests" error. This error is your cue to pause and retry later. To monitor your usage, check the X-HubSpot-RateLimit-Remaining and X-HubSpot-RateLimit-Max headers in your API responses. The X-HubSpot-RateLimit-Remaining header shows how many requests you have left in the current 10-second window, while X-HubSpot-RateLimit-Max indicates the total allowed. If the remaining count hits zero, you’ve reached the burst limit.
You can also track API usage in the HubSpot UI under Development > Monitoring > API call usage. For certified apps listed in the HubSpot Marketplace, it’s critical to keep error rates (including 429 errors) below 5% of total daily requests. This means maintaining a success rate of at least 95%. If you’re processing large volumes of data too quickly, you might also encounter a 423 Locked error. In such cases, you’ll need to wait at least 2 seconds before retrying.
By using these monitoring tools, you can identify when throttling occurs and take steps to minimize it.
Techniques to Reduce API Throttling
Reducing the total number of API requests is the most effective way to avoid throttling. Here are some strategies:
- Batch requests: Instead of sending individual updates for multiple records, group them into a single batch request. For example, update 100 contacts in one go rather than one at a time.
- Webhooks over polling: Webhooks let HubSpot push updates to your system when changes happen. These calls don’t count toward your API rate limits.
- Local caching: Cache static data locally to avoid making redundant API calls.
If you do encounter a 429 error, always respect the Retry-After header, which specifies how long to wait before making another request. For integrations with multiple parallel processes, consider using a token bucket algorithm. This approach centralizes API calls, ensuring all processes stay within the burst limit.
sbb-itb-69c96d1
Data Synchronization and Duplicate Records
Once API rate limits are under control, the next hurdle is ensuring your data stays consistent. Duplicate records can clutter up your CRM and distort your reports, often stemming from mismatched record identifiers. For example, HubSpot identifies contacts by email addresses, while systems like Salesforce might allow multiple contacts with the same email. When syncing these systems, duplicates can pile up quickly.
Another sneaky source of duplicates is the "Automatically create and associate companies with contacts" setting in HubSpot. If this feature is enabled, it can create duplicate company records during synchronization. For instance, if a Salesforce account already exists but HubSpot generates a new record from a form submission or email tracking, you could end up with two company records for the same entity. While HubSpot deduplicates companies based on Salesforce Account ID or domain, it doesn’t automatically handle duplicate deals linked to Salesforce opportunities. This can result in new records being created in both systems by default.
The type of API operation you choose also plays a role. Using CREATE instead of UPSERT can lead to duplicate records if the data already exists. The UPSERT operation, on the other hand, checks for existing records before adding new ones, making it a safer option for imports. Additionally, HubSpot allows you to define up to 10 custom unique identifier properties per object by setting the hasUniqueValue attribute to true. This feature is particularly handy when syncing with third-party systems that rely on their own unique IDs.
Preventing Duplicate Records
To tackle these issues, you’ll need strategies to stop duplicates at the source. One effective method is using the batch upsert endpoint (/crm/v3/objects/contacts/batch/upsert) to update existing records instead of creating duplicates. When making API calls, specify a custom unique ID with the idProperty parameter (e.g., ?idProperty=internal_customer_id) instead of relying solely on the HubSpot Object ID.
It’s also important to clean your source data before syncing. Deduplicate records in your "source of truth" system, such as Salesforce, and designate a primary record there before syncing with HubSpot. To avoid redundant company records, consider disabling the "Automatically create and associate companies with contacts" setting when integrating HubSpot with external CRMs.
Here’s a quick reference for unique identifiers across HubSpot objects:
| Object Type | Primary Unique Identifier | Secondary/Custom Identifiers |
|---|---|---|
| Contacts | Email Address (email) |
hs_object_id, Custom unique properties |
| Companies | Company Domain Name (domain) |
hs_object_id, Salesforce Account ID |
| Deals | HubSpot Object ID (hs_object_id) |
Custom unique properties |
Finally, focus on updating only the records that have changed.
Using Incremental Syncs
Instead of re-importing your entire database, switch to incremental syncs. This method updates only the records that have been modified, reducing API calls, speeding up sync times, and cutting down on duplicates. Use the hs_lastmodifieddate field as a filter - store the timestamp of your last successful sync and apply a "greater than" filter through the Search API to capture only updated records.
For real-time updates, webhooks are a great option. They notify you whenever data changes in HubSpot and don’t count toward your API rate limits, making them ideal for high-volume integrations. When working with large datasets, use the after parameter for paging through batch endpoints (limited to 100 records per request) to keep things running smoothly. The HubSpot Imports API can process up to 80,000,000 rows per day, though individual files are capped at 1,048,576 rows or 512 MB.
Error Handling and Retry Logic
Once token management, field mapping, and rate limiting are in place, the next step is ensuring robust error handling to maintain integration stability.
Network issues are inevitable, and HubSpot uses standard HTTP status codes to signal problems. 4xx codes indicate client-side errors like bad requests or missing permissions, while 5xx codes point to server-side issues. Each error response includes a correlationId, which is crucial for troubleshooting persistent problems with HubSpot support.
For transient errors, such as 429, 500, 502, 503, and 504, automatic retries are essential. However, avoid retrying errors like 401 and 403, as they often require manual intervention.
Typical Integration Errors
HubSpot's error responses come with a JSON body detailing fields like status, message, correlationId, and category to help identify the issue. For CRM object APIs, additional fields like code and context specify which properties have issues. For example:
- A
400 Bad Requestusually points to syntax errors in the request body. - A
403 Forbiddenerror means your token lacks the required permissions, such as thecrm.objects.deals.readscope for accessing the Deals API.
HubSpot also has some unique error codes:
423 Locked: This happens when too many records are upserted too quickly. The error typically resolves within 2 seconds.477 Migration in Progress: Indicates an account is being moved between data centers. The response includes aRetry-Afterheader with wait times that can extend up to 24 hours.414 Request-URI Too Large: Happens when the request URL is excessively long. Shorten query parameters or reduce payload size to resolve it.524 Timeout: Triggered by HubSpot's 100-second response timeout for long-running processes.
For batch operations, HubSpot may return a 207 Multi-Status response, indicating partial success. This allows you to pinpoint which records failed during a large batch operation.
| Error Code | Meaning | Primary Trigger |
|---|---|---|
400 |
Bad Request | Syntax errors/malformed request |
401 |
Unauthorized | Invalid/expired credentials |
403 |
Forbidden | Missing required scopes |
423 |
Locked | High-volume upserts |
429 |
Too Many Requests | Rate limits exceeded |
477 |
Migration in Progress | Data center migration |
502/504 |
Timeouts | Server overload |
These error details enhance your ability to respond quickly and recover automatically.
Building Reliable Error Recovery
When designing retry logic, implement exponential backoff with jitter. For a 429 error, use the Retry-After header to determine the wait time. HubSpot typically provides this value in seconds for most APIs, but in milliseconds for workflow-based webhooks. For 5xx errors like 502, 503, or 504, introduce a brief pause before retrying to allow the server time to stabilize. Adding jitter - randomized delays - prevents multiple servers from retrying simultaneously and overwhelming the API.
To avoid duplicate records during retries, ensure operations are idempotent by using UPSERT logic.
"This [500 internal error] is a transient error that can appear randomly depending on the number of API requests we are receiving at that time. In situations like this, the integration will need to send the API request again after a short delay." - Pam Cotton, HubSpot Alumni
Proactively refreshing tokens can help prevent 401 errors. Instead of waiting for an Unauthorized response, monitor the expires_at timestamp and refresh OAuth tokens 5 minutes before expiration. In multi-server setups, use a distributed lock (e.g., Redis) during token refreshes to avoid race conditions where multiple servers attempt to refresh the same token simultaneously.
For webhook integrations, ensure your system returns a 200 OK within 5 seconds of receiving notifications, then process the data asynchronously. This prevents HubSpot from retrying successful deliveries. Failed notifications will prompt retries up to 10 times over 24 hours. Set HTTP request timeouts between 10–30 seconds, and use structured logging in JSON format to track error patterns. Keeping your error rate below 5% of total daily requests is crucial for apps aiming for HubSpot App Marketplace certification.
When to Partner with Vestal Hub for Complex Integrations
If your team is facing persistent integration headaches that standard troubleshooting can't fix, it might be time to bring in the experts. While basic integrations work fine for most setups, certain red flags - like an error rate exceeding 5% or scaling across multiple servers that triggers race conditions in in-memory token caching - are clear signs that a DIY approach may no longer cut it. These kinds of challenges demand a professional touch.
What Vestal Hub Brings to the Table
For advanced integration issues - like token expiry problems or field mapping errors - Vestal Hub steps in with tailored solutions. They specialize in tackling the kind of roadblocks that can overwhelm internal teams, offering services like custom API development, middleware solutions, and unified data architecture specifically designed for complex B2B SaaS environments using HubSpot.
One of the standout features Vestal Hub provides is its ability to address 429 rate limit errors. These errors, caused by exceeding limits like 100 requests per 10 seconds for standard accounts, can bring scaling efforts to a halt. Vestal Hub counters this with tools like request queuing, adaptive throttling, batch APIs, and intelligent caching to keep things running smoothly.
Security is another area where Vestal Hub shines. They validate webhook signatures using HMAC SHA-256 and implement robust error recovery mechanisms. For example, they handle 423 Locked errors, which typically resolve within 2 seconds, and 477 Migration errors, which may take up to 24 hours to address.
On top of that, Vestal Hub manages cloud-hosted OAuth services, ensures bidirectional syncs with conflict resolution, and tracks batch failures using objectWriteTraceId. This level of technical expertise ensures that your data flows seamlessly, even during the most critical operations.
Summary
One of the main culprits behind request denials is expired credentials. To avoid 401 errors, make sure to automate token refreshes before the 30-minute expiration window closes. Additionally, standard HubSpot accounts have a limit of 100 requests per 10 seconds. Exceeding this threshold results in 429 errors, which can disrupt data synchronization. Developers who are well-versed in HTTP response codes can resolve integration issues up to 40% faster. Techniques like exponential backoff with jitter and leveraging batch APIs are key to staying within these rate limits.
Operational challenges often arise from field mapping errors and duplicate records. These issues occur when internal property IDs don’t align with HubSpot’s schema or when lifecycle stages are updated incorrectly. To minimize 400 Bad Request errors, rely on incremental syncs using the hs_lastmodifieddate property and validate payloads against JSON schemas before sending requests. These practices significantly enhance integration reliability.
For production-grade integrations, error rates above 5% often point to deeper architectural flaws. Address these by implementing distributed caching solutions like Redis, validating webhook signatures, and using intelligent retry logic. For instance, handle 423 Locked errors with a brief 2-second delay and prepare to wait up to 24 hours for 477 Migration errors to resolve.
Lastly, continuous monitoring is critical for maintaining a stable API integration. Use HubSpot’s "Monitoring > API call usage" dashboard to track activity, enable structured logging to capture raw request and response data, and always test thoroughly in sandbox environments before deploying to production. If your team is stretched too thin or scaling becomes challenging, consider partnering with experts like Vestal Hub to ensure your HubSpot CRM remains a seamless part of your operations without interruptions.
FAQs
How do I avoid token expiration problems when integrating with the HubSpot API?
When working with HubSpot API integration, it's crucial to securely store the refresh token you receive during the OAuth authentication process. This token allows you to request a new access token before the current one expires, ensuring your integration keeps running smoothly without interruptions.
By managing tokens effectively, you can maintain consistent performance and avoid manual intervention, even during extended periods of inactivity. Thoughtful token management is essential for keeping your API integration running seamlessly.
How can I effectively manage HubSpot API rate limits?
To handle HubSpot API rate limits effectively, try these practical approaches:
- Use exponential backoff: When an API request hits a rate limit, retry it after progressively longer intervals. This method prevents overwhelming the system and lowers the chances of repeated errors.
- Time your requests wisely: Review your API usage to identify peak activity times and spread out requests more evenly. This can be especially helpful during high-demand periods, like marketing campaigns.
- Implement caching: Save frequently accessed data locally to cut down on repetitive API calls. This reduces unnecessary requests and helps you stay within allowed limits.
- Batch your operations: Whenever possible, combine multiple tasks into a single API call. This approach maximizes efficiency and keeps your system running smoothly.
Using these strategies together can help you optimize API usage and maintain seamless HubSpot integrations.
How can I ensure accurate field mapping to prevent data sync issues with HubSpot?
To keep your field mapping accurate and prevent data sync errors with HubSpot, start by aligning the source attributes directly with the target properties in HubSpot. Skip any unnecessary conversions - they often lead to errors that could have been avoided.
Pay close attention to the format of critical data types like numbers, dates, and currencies. Sync failures often stem from mismatched formats, so ensuring compatibility here is key. Before committing to a full data transfer, run small-scale batch tests with portions of your data. This approach helps spot and fix mapping issues early.
Finally, take the time to document all your mapping choices. A well-documented process makes troubleshooting or adjusting mappings down the line much simpler.